The human body is a marvel of intricate design and functionality, where every system works in harmony to maintain optimal health. One essential component of our physiology is the muscular system, responsible for movement, strength, and stability. However, there are instances when this vital system experiences challenges, leading to a condition known as muscle wasting. In this article, we will delve into the topic of muscle wasting, exploring its symptoms, implications, and potential causes.
Unveiling the Symptoms of Muscle Wasting
Muscle wasting, also referred to as muscle atrophy, occurs when the muscle fibers begin to shrink or waste away, resulting in a gradual loss of muscle mass and strength. Recognizing the symptoms of muscle wasting is crucial for early detection and intervention. One of the most apparent signs is a noticeable decrease in muscle size and overall strength. Individuals affected by muscle wasting may experience difficulty in performing everyday tasks that were once routine, such as lifting objects or climbing stairs.
In addition to physical changes, muscle wasting often manifests through a decline in physical endurance and increased fatigue. Individuals may find themselves becoming easily exhausted, even after minimal exertion. Furthermore, muscle wasting can lead to a reduction in mobility and flexibility, making movements feel stiff and restricted. As these symptoms progress, individuals may notice a general decline in their physical performance and overall quality of life.
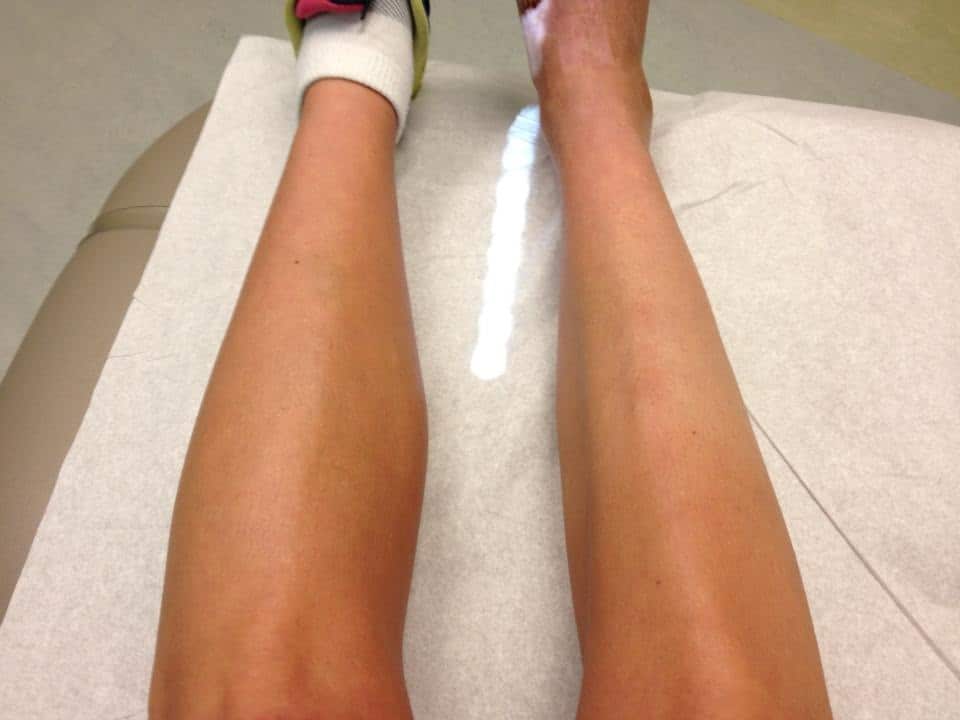
Underlying Causes and Implications
Muscle wasting can arise from various factors, each with its own set of implications. One common cause is disuse atrophy, which occurs when muscles are not regularly used or stimulated. Prolonged bed rest, sedentary lifestyles, or being in a cast due to an injury can contribute to muscle wasting. Neurogenic atrophy, another type of muscle wasting, is often associated with conditions that affect the nervous system, such as spinal cord injuries, stroke, or neuropathy.
Additionally, certain medical conditions and diseases can lead to muscle wasting. Cancer, particularly in advanced stages, can cause muscle atrophy as the body redirects resources to fight the disease. Chronic illnesses like HIV/AIDS, kidney disease, and congestive heart failure can also contribute to muscle wasting. Furthermore, malnutrition and inadequate protein intake can deprive the body of the essential building blocks needed for muscle maintenance, leading to muscle wasting.
The implications of muscle wasting extend beyond physical limitations. Individuals affected by muscle wasting often experience a significant decrease in their overall quality of life. Loss of independence, diminished mobility, and decreased self-esteem can impact mental and emotional well-being. Muscle wasting can also lead to a higher risk of falls, fractures, and other injuries, further exacerbating the challenges faced by those affected.
Addressing Muscle Wasting and Promoting Muscle Health
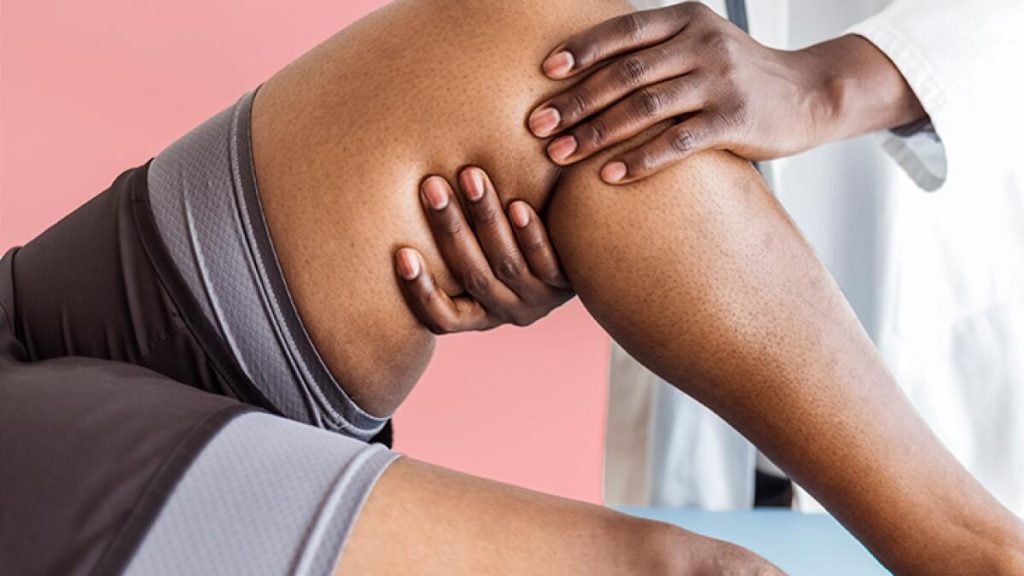
While muscle wasting can be a complex and multifaceted condition, there are steps individuals can take to mitigate its effects and promote muscle health. Regular physical activity, particularly exercises that target muscle strength and endurance, can help counteract muscle wasting. Engaging in resistance training, such as weightlifting or using resistance bands, stimulates muscle growth and reduces muscle loss.
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for preserving muscle mass. Adequate protein intake is particularly important, as proteins serve as the building blocks for muscle repair and growth. Including lean sources of protein, such as chicken, fish, legumes, and tofu, can support muscle health. Additionally, staying hydrated and consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables ensures a supply of essential vitamins and minerals necessary for optimal muscle function.
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to address underlying causes of muscle wasting. Physical therapy, medications, and, in certain instances, surgical interventions can help manage muscle wasting and improve overall muscle function. Seeking professional medical advice and guidance is essential to develop an individualized approach that addresses the underlying causes and specific needs of each individual.
Conclusion
Muscle wasting is a complex condition with various causes and implications. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the underlying causes, and taking proactive steps to address muscle wasting are crucial for maintaining muscle health and overall well-being. By prioritizing physical activity, proper nutrition, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can reduce the impact of muscle wasting and enhance their quality of life. Remember, your muscles are a remarkable part of your body, and by nurturing and caring for them, you can continue to enjoy a life full of strength and vitality.

